The MRC National Survey of Health of Development (NSHD) assessed their cohort members (CMs) during the study’s age 53 sweep using the Verbal Learning/Word List Recall Test.
Details on this measure and the data collected from the CMs are outlined in the table below.
| Domain: | Verbal (memory) |
| Measures: | Verbal memory |
| Attention | |
| Short-term episodic memory | |
| Free-recall memory | |
| CHC: | Glr (Long-Term Storage and Retrieval) |
| Administration method: | Research nurse; face to face; pen and paper |
| Procedure: | Same as for age 43, however, a delayed recall condition was also added; participants were asked to recall the words again after the letter search task (an interval of approximately 90 seconds). A different word list was given to each half of the cohort at 43 years and these lists were reversed when they were at 53 years of age, to minimize any practice effects. |
| Link to questionnaire: | https://skylark.ucl.ac.uk/NSHD/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=questionnaires:1999-capi.pdf (opens in new tab) |
| Scoring: | A point was awarded for every correct word recalled (0 - 45 [immediate]; 0 - 15 [delayed]). |
| Item-level variable(s): | wlin199 - wltx99 |
| Total score/derived variable(s): | WLT99 |
| Descriptives: | Raw score |
| N = 2,887 | |
| Range = 3 - 41 | |
| Mean = 23.93 | |
| SD = 6.30 | |
(click image to enlarge)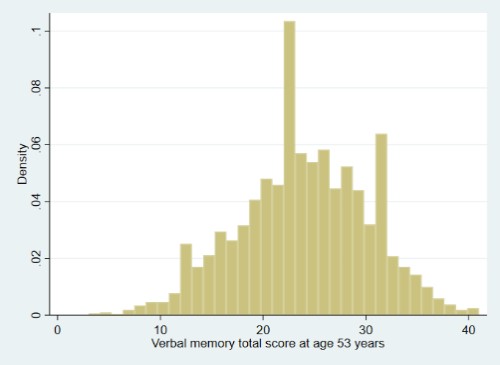 |
|
| Age of participants (months): | Mean = 641.47, SD = 2.09, Range = 636 - 650 |
| Other sweep and/or cohort: | NCDS – Age 50 – Verbal Learning/Word List Recall Test (Immediate and Delayed) (1 trial only; 10 words, presented aurally) |
| NCDS – Age 61-63 – Proposed repeat of tests at age 50 | |
| BCS70 – Age 46-47 – Verbal Learning/Word List Recall Test (Immediate and Delayed) (1 trial only; 10 words, presented aurally) | |
| NSHD – Age 43 – Verbal Learning/Word List Recall Test | |
| NSHD – Age 60-64 – Verbal Learning/Word List Recall Test | |
| NSHD – Age 68-70 – Verbal Learning/Word List Recall Test | |
| Source: | This task was developed specifically for this study by the NSHD team led by Prof Bryan Rodgers. Similar tasks have been used to measure verbal learning for decades, e.g. Bush and Mosteller (1955). |
| Technical resources: | None |
| Reference examples: | Richards, M., Hardy, R., & Wadsworth, M. E. (2004). Alcohol consumption and midlife cognitive change in the British 1946 birth cohort study. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 40(2), 112-117. |
| Richards, M., Shipley, B., Fuhrer, R., & Wadsworth, M. E. (2004). Cognitive ability in childhood and cognitive decline in mid-life: longitudinal birth cohort study. BMJ, 328(7439), 552. |
Go to:
- Overview of all cognitive measures in NSHD
- Overview of adulthood cognitive measures across all studies
This page is part of CLOSER’s ‘A guide to the cognitive measures in five British birth cohort studies’.
